Introduction
Apache Spark has become one of the most popular tools for running analytics jobs. This popularity is due to its ease of use, fast performance, utilization of memory and disk, and built-in fault tolerance. These features strongly correlate with the concepts of cloud computing, where instances can be disposable and ephemeral.
In this lecture, we’re going to run our spark application on Amazon EMR cluster. Also, we’re going to run spark application on top of the Hadoop cluster and we’ll put the input data source into the s3. Furthermore, you might want to ask why we need to save our input source file into s3 instead of local disk this is because in the real world we want to make sure that our data is coming from some distributed file system that can be accessed by every node on our spark cluster.
What is Amazon EMR
EMR stands for elastic Map Reduce. Amazon EMR cluster provides up managed Hadoop framework that makes it easy fast and cost-effective to process vast amounts of data across dynamically scalable Amazon ec2 instances. Also, we can also run other popular distributed frameworks such as Apache spark and HBase in Amazon EMR and interact with data and other AWS data stores such as Amazon s3 and Amazon DynamoDB.
In other words, Amazon EMR is a managed cluster platform that simplifies running big data frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, on AWS to process and analyze vast amounts of data. By using these frameworks and related open-source projects, such as Apache Hive and Apache Pig, you can process data for analytics purposes and business intelligence workloads
Our Goal
Our goal is to parse a couple of log files amounting to several thousands of records. This will be done using a hive script/spark program. An SQL table will be created with this structure then the file will be parsed based on this regular expression. Finally, the query will output the number of total requests per operating system
Processing Pipeline
Before diving into the task, let us set up a small pipeline to achieve our goal.
- Setting up EMR clusters: We will create an EMR cluster first running different EC2 instances. These clusters will have the capability of providing a scalable and distributed platform for running our code to process big data
- Attaching a Data Source
- Setting up the Runner Task
- Viewing Results and Terminating the EMR Cluster
Step 1: Creating an EMR Cluster
You need to go to the AWS management console. After then, click services on the top left. Then you need to select EMR.
Now we’re at the EMR page. You need to click create a cluster.
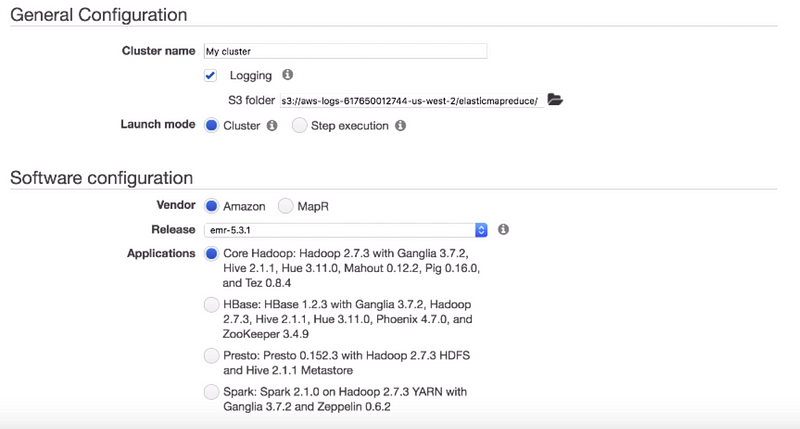
We can leave the cluster name as default. There are two launch modes i.e cluster mode and step execution. With cluster mode, EMR will create a cluster with a set of specified applications. You can add steps to the cluster. After it’s launched, the cluster continues running until you terminate it with stop execution. In our case, we want to install SPARK on top of the Hadoop cluster and we don’t want the cluster to terminate automatically after the job is done so we choose the cluster mode.
This vendor option sets the vendor from which you want to select the software release and applications for your cluster. This release option specifies the software and Amazon EMR platform components to install on the cluster. Amazon EMR uses the release to initialize the Amazon ec2 instances on which your cluster runs. The latest release label is selected by default. We will leave it as default. The application option determines the applications to install on your cluster. Here, we want to install SPARK on top of it.
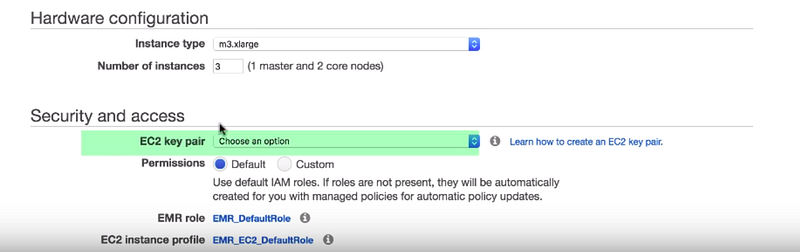
The instant type option determines the Amazon ec2 instance type that Amazon EMR initializes for the instances that run in your cluster. We will use the default. The ec2 key pair option specifies the Amazon ec2 key pair to use when connecting to the nodes in your cluster using SSH. if we do not select the key pair you cannot connect to the cluster. For the rest of the permissions, we go with the default options. After that, we click to create a cluster to start the provisioning now as you see the cluster is in starting state which means the cluster is been provisioned this process takes about 10 to 15 minutes to complete after the cluster is successfully created the state will turn from starting to waiting
Step 2: Preparing Datasource
Next, let’s prepare our input data source. We will be using the StackOverflow survey data for this demo. You can find it here. Since we’re going to run our SPARK application on a much large cluster on AWS we can analyze the full stack overflow server data source.
Here on stack overflow research page, we can download data source. After the download is complete, you see the full stack overflow server data source is in CSV format. Next, we’ll be uploading this file to s3.
You need to log into the AWS management console again and select s3. Let’s create a new s3 bucket for our spark job. A bucket is a logical unit of storage in s3. Objects are created under buckets. Here, we name our s3 bucket StackOverflow — analytics and then click create.
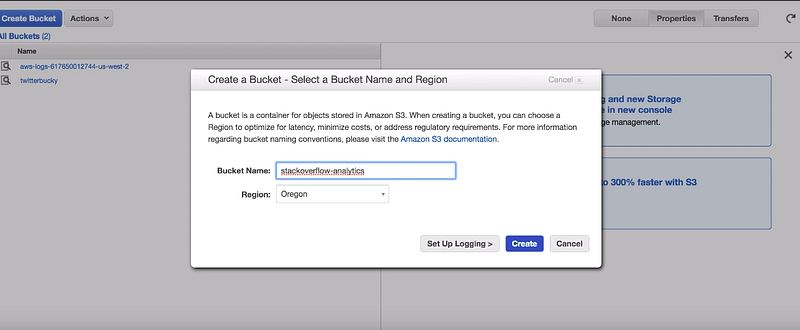
Now we can just select the newly created bucket name then click upload. After the uploading is complete we can see the CSV file appears under the bucket.
Step 3: Setting up the task
Since data source is ready on s3 let’s login into the spark master machine via SSH. You can find the ssh command by clicking the SSH link under our cluster page. Copy the SSH command and paste it into a terminal. Furthermore, make sure there is an ec2 private key file at the path to the private key file.
ssh -i ~/myKey.pem hadoop@ec2-45-218-54-34.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com
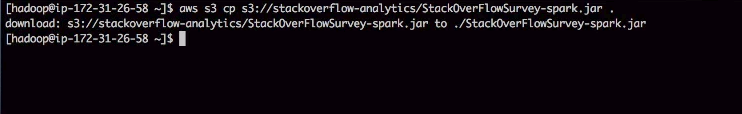
Let’s fetch the jar file from s3 to the master machine here for execution. We run AWS s3 CP command which can copy files from or to s3 then supply the source file path which is the s3 file path.
aws s3 cp s3://stackoverflow-analytics/StackOverflowSurvey-Spark.jar .
Now we can just run sparks emit and put the jar file name as an argument and hit enter.
Step 4: Terminating the clusters
By running it, we get all the job outputs now we have seen how to run our spark application on a remote cluster.
Make sure you delete all the files from s3 and terminate your EMR cluster if you don’t need them anymore otherwise it would cost money that’s it
Summary
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances offer spare compute capacity available in the AWS Cloud at steep discounts compared to On-Demand prices. EC2 can interrupt Spot Instances with two minutes of notification when EC2 needs the capacity back. You can use Spot Instances for various fault-tolerant and flexible applications. Some examples are analytics, containerized workloads, high-performance computing (HPC), stateless web servers, rendering, CI/CD, and other test and development workloads.
Amazon EMR provides a managed Hadoop framework that makes it easy, fast, and cost-effective to process vast amounts of data using EC2 instances. When using Amazon EMR, you don’t need to worry about installing, upgrading, and maintaining Spark software (or any other tool from the Hadoop framework). You also don’t need to worry about installing and maintaining underlying hardware or operating systems. Instead, you can focus on your business applications and use Amazon EMR to remove the undifferentiated heavy lifting.
Follow this link, if you are looking to learn more about data science online!
You can follow this link for our Big Data course!
Additionally, if you are having an interest in learning Data Science, Learn online Data Science Course to boost your career in Data Science.
Furthermore, if you want to read more about data science, you can read our blogs here

