Introduction:
Setting up a new business? Or trying to grow an existing one? No matter which one it is, web scraping is the best way to collect data for growing your business today. It will help you get valuable insights, and information about your latest competition, no matter what you deal in – products or services. Although web scraping has been going on for quite some time, it has never been as heavily used, or as reliable as it is today.
In this blog, we will learn about web scraping. Furthermore, we will also learn about making our own web scraper and collect data from the websites. We will implement the scraper in python using the Beautiful Soup library. So before we jump into web scraping, let us first understand what web scraping actually is!
What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites. All the job is carried out by a piece of code which is called a “scraper”. First, it sends a “GET” query to a specific website. Then, it parses an HTML document based on the received result. After it’s done, the scraper searches for the data you need within the document, and, finally, convert it into the specified format.
Web-scraping is an important technique, frequently employed in a lot of different contexts, especially data science and data mining. Python is largely considered the go-to language for web-scraping, the reason being the batteries-included nature of Python. With Python, you can create a simple scraping script in about 15 minutes and in under 100 lines of code. So regardless of usage, web-scraping is a skill that every Python programmer must have under his belt.
Uses of Web Scraping:
These include article extraction for websites that curate content, business listings extraction for companies that build databases of leads, and many different types of data extraction, sometimes called data mining. For example, one popular and sometimes controversial use of a web scraper is for pulling prices off of airlines to publish on airfare comparison sites.
Scraping Goal
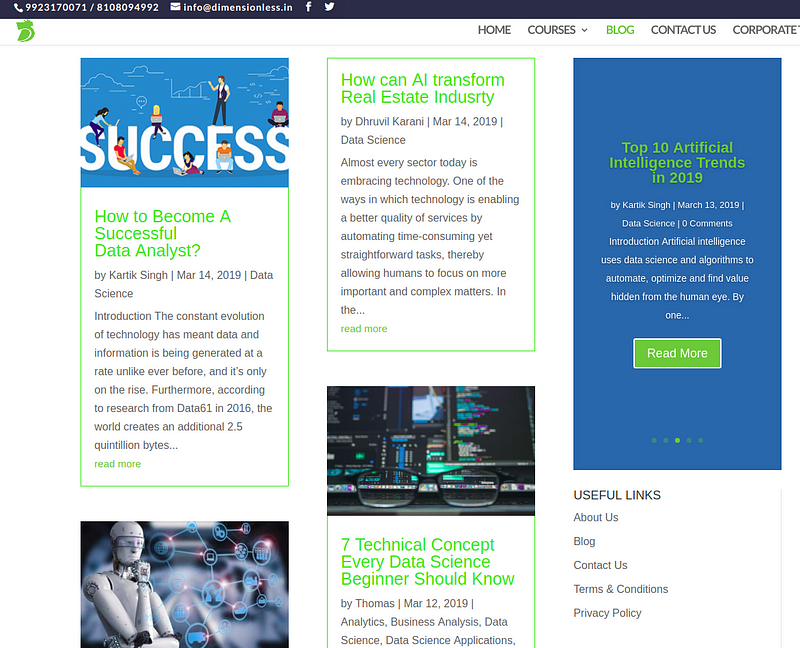
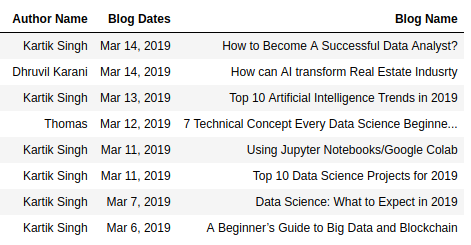
In this blog, we will try to learn about web scraping by implementing it ourselves. Our goal is simple here. We have a blog section on our website. What we want is fairly simple. We need the data containing blog title, date, and the author name.
The target page looks like one below. You can visit the page through the following link.
The Web Scraping Pipeline:
Before we directly jump to web scraping, let us have a look at the basic pipeline for this. We can understand web-scraping as a pipeline containing 3 components:
- Downloading: Downloading the HTML web-page
- Parsing: Parsing the HTML and retrieving data we’re interested in
- Storing: Storing the retrieved data in our local machine in a specific format
In the next section, we will implement a web scraper to get all the blog names for us using python. We will use Beautiful Soup library in python for scraping web pages. One by one, we will go through the stages in the scraping pipeline. Full code will be present in the end section.
Implementing a Web Scraper using Beautiful Soup:
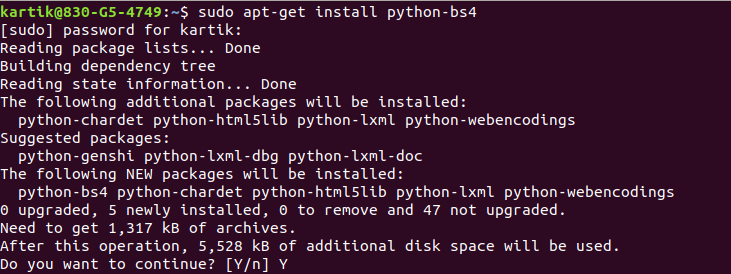
First of all, we need to install Beautiful Soup library in our system. To install it, you can use the following command
## Using apt-get sudo apt-get install python-bs4
## Using pip pip install bs4
Once you run the above command, it will start installing the packages for you.
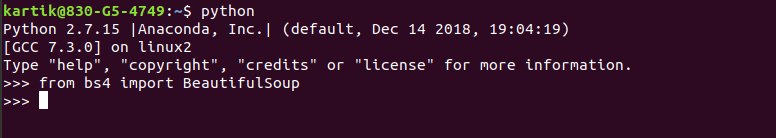
In order to verify the installation, you can try importing the library following way
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
Let us start writing our scraper now. You need to analyze the HTML structure of the target web page. To do so, you can left click and select inspect element option. This will enable you to see the HTML code behind the web page.
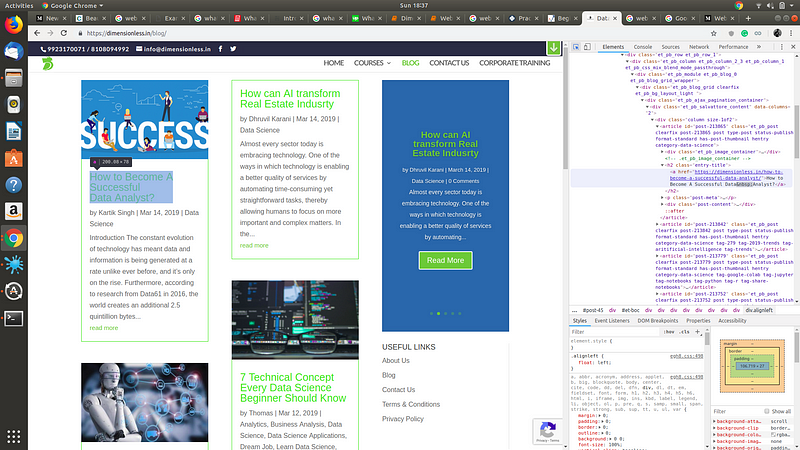
With the pen icon button, you can hover over the website to find their code in the source code. For example, to find the HTML code for the author name, hover the mouse over the author name. On the right side, it will highlight for you the location of that code.
Let us dig deeper into the HTML code here.
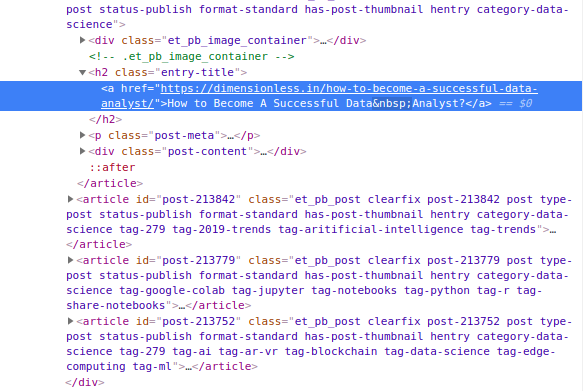
After hovering over the author name, we can clearly see the HTML code here for the same. All the author names have an H2 tag with class name “entry-title”. We can use this combination of tag and class name to get all the instances where the author name is there. A similar process will happen for the date and the author name.
We can start building our scraper now. First, we need to import all the basic libraries. We can do this by the following code
## For downloading HTML structure import requests
## For Scraping through HTML from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
## For visualising data in a table import pandas as pd
Downloading the Data:
Once we have all the libraries, we start by downloading the HTML code of the target website. Now, we need to mention our target URL. After that, we need to download the HTML content from the target web page. In the end, we will have an object(Beautiful soup compatible) holding the data.
## Mentioning the target url targetUrl = 'https://dimensionless.in/blog'
## Downloading the HTML content from the target page r= requests.get(targetUrl) data=r.text
##Converting the data into a Beautiful Soup compatible object soup=BeautifulSoup(data)
Parsing the Data:
Once we have the entire HTML content available, we need to search for our specific information in this data. As we saw earlier, we can use the tag type and other identifiers like id or class to extract any specific information.
Upon exploring the code, I was able to find the following identifiers for our target information. You can also try to find out these using inspect elements. Try to analyze that this selection makes sense or doesn’t make sense.
Blog Name — — Tag-”H2″ — — class-”entry-title”
Author Name — — Tag-”span” — — class-”author vcard”
Blog Date — — Tag-”span” — — class-”published”
## Lists for holding the values blog_names=[] author_names=[] blog_dates=[]
## Iterating through all the articles and extracting blog title, author name and blog date
for listing in soup.find_all('article'):
for blog_name in listing.find('h2', attrs={'class':"entry-title"}):
blog_names.append(blog_name.text)
for author_name in listing.find('span', attrs={'class':"author vcard"}):
author_names.append(author_name.text)
for blog_date in listing.find('span', attrs={'class':"published"}):
blog_dates.append(blog_date)
Visualising and Storing Results:
In the previous step, we have collected the data from the website using the code. Now, it is time to see the data. This task is fairly simple. You can use the pandas library available in python to store all the results in a table (data frame). The following code will perform this task for you!
blogData=pd.DataFrame({"Blog Name":blog_names, "Author Name":author_names, "Blog Dates":blog_dates})
Furthermore, you can find the full code below
## For downloading HTML structure import requests ## For Scraping through HTML from bs4 import BeautifulSoup ## For visualising data in a table import pandas as pd ## Mentioning the target url targetUrl = "https://dimensionless.in/blog" ## Downloading the HTML content from the target page r= requests.get(targetUrl) data=r.text ##Converting the data into a Beautiful Soup compatible object soup=BeautifulSoup(data) ## Lists for holding the values blog_names=[] author_names=[] blog_dates=[] ## Iterating through all the articles and extracting blog title, author name and blog date for listing in soup.find_all('article'): for blog_name in listing.find('h2', attrs={'class':"entry-title"}): blog_names.append(blog_name.text) for author_name in listing.find('span', attrs={'class':"author vcard"}): author_names.append(author_name.text) for blog_date in listing.find('span', attrs={'class':"published"}): blog_dates.append(blog_date) blogData=pd.DataFrame({"Blog Name":blog_names, "Author Name":author_names, "Blog Dates":blog_dates})
The Advantages of Web Scraping:
The major advantages of web scraping services are:
- Inexpensive — Web scraping services provide an essential service at a low cost. It is paramount that data is collected back from websites and analyzed so that the internet functions regularly. Web scraping services do the job in an efficient and budget-friendly manner.
- Easy to Implement — Once a web scraping services deploy the proper mechanism to extract data, you are assured that you are not only getting data from a single page but from the entire domain. This means that with just a onetime investment, a lot of data can be collected.
- Low Maintenance and Speed– One aspect that is often overlooked when installing new services is the maintenance cost. Long term maintenance costs can cause the project budget to spiral out of control. Thankfully, web scraping technologies need very little to no maintenance over a long period. Another characteristic that must also be mentioned is the speed with which web scraping services do their job. A job that could take a person week is finished in a matter of hours.
- Accuracy — The web scraping services are not only fast, but they are also accurate too. Simple errors in data extraction can cause major mistakes later on. Accurate extraction of any type of data is thus very important. In websites that deal in pricing data, sales prices, real estate numbers or any kind of financial data, the accuracy is extremely important.
Summary
In this blog, we learned about scraping web pages in python. We used BeautifulSoup library to perform the scraping for us. Web scraping is one of the most important methods of collecting data online. Let us touch upon a concept that often comes up and confuses most of us when we read about Web scraping: web crawling! So, what is web crawling? Web crawling entails downloading a web page’s data automatically, extracting the hyperlinks on the same and following them. This downloaded data can be organized in an index or a database, using a process called web indexing, to make it easily searchable. How are the two techniques different? In simple terms, you can use web scraping to extract book reviews from the Goodreads website to rate and evaluate books. You can use this data for an array of analytical experiments. On the other hand, one of the most popular applications of a web crawler is to download data from multiple websites and build a search engine. Googlebot is Google’s own web crawler.
Follow this link, if you are looking to learn more about data science online!
You can follow this link for our Big Data course!
Additionally, if you are having an interest in learning Data Science, Learn online Data Science Course to boost your career in Data Science.
Furthermore, if you want to read more about data science, you can read our blogs here

