Introduction
Connecting our brains to the machine and saving memories for a lifetime was one of the tasks scientists have been chasing after for so long. But all this may come to life now! With Elon and his new venture of uniting man and machine together, Musk briefed the entire world about how he can connect our brains to computers and digitise the control through brains and much more! In July of 2019, Elon Musk had a presentation detailing the neural link project. Earlier in the year, musk had said that there are some big announcements coming and this was it. It was all about neuralink and world of possibilities which it brings along!
After watching the presentation and thinking about it a little bit, a lot of this stuff has actually been done before. It’s nothing new. It’s just been done a lot better! So let’s take a look at what the neuralink is how it works and the new future that we could all be facing.
About Neuralink company
Neuralink is a neuroprosthetics corporation working on implantable Brain-computer interfaces. Founded by Elon Musk, Ben Rapoport, Dongjin Seo and others, the company boasts of having several high profiles neuroscientists across the world.
In the short term,company intends to produce devices for the treatment and eventual human enhancement, often called transhumanism, of severe brain diseases. The initial aim of the company is to build a module located outside the head gets data via wireless from small elastic, brain-integrated electrode strands which can be termed as the technology for the future.
What is the Neuralink product
The theory states that human cognition has two major systems. It consists of the limbic system where our emotions needs and once are processed and then the cortex which involves thinking and planning. The neural link in, its final form, is to be the third layer on top of this a digital super-intelligence layer augmenting ourselves with computers. It will become eventually an artificial intelligence depending on how you look at it. We already have this layer in the form of our phones and laptops. You’ve all heard the saying that we have all of the world’s information at our fingertips. The bottleneck and all of this is how we interface with that information. fingers and speech are too slow and have a very low bandwidth form of communication between us and our devices.
A much faster way to get to this information would be directly from the brain and this is called the brain-machine interface (BMI) and the neural link is an effort to solve this problem. it’s already been a massive the multidisciplinary effort it includes scientists, doctors, electrical engineers, surgeons and more.
So how does it work? Our brain consists of neurons firing all the time in response to electrical signals sent. When we see, move talk or think, a neuron fires from these electrical signals. A tiny electromagnetic field is present to tap into these tiny generated neuron signals.
The brain is going to interpret this analogue data as ones and zeros to be used in the digital world. The neuron pulses will be detected using tiny threads (about one-tenth the cross-section of a human hair) each thread is to be installed with a robot so it’s not going to burst blood vessels or cause trauma
The needle for insertion is 24 microns in diameter which is much smaller than the state-of-the-art in deep brain stimulation. Such surgeries have been done before for deep brain stimulation on Parkinson’s sufferers. Through these traditional methods, we have a 1 in 100 chance of causing a severe brain haemorrhage. A smaller footprint should make things much safer. The state of the art for Parkinson’s deep brain stimulation has around 10 electrodes. The neural link contains thousands of electrodes. These electrodes need to be less than 60 microns away to detect a fire in neuron and serve as an interface that reads data from the brain and sends data to the brain. The processor for making all of this work is something called the n1 chip.
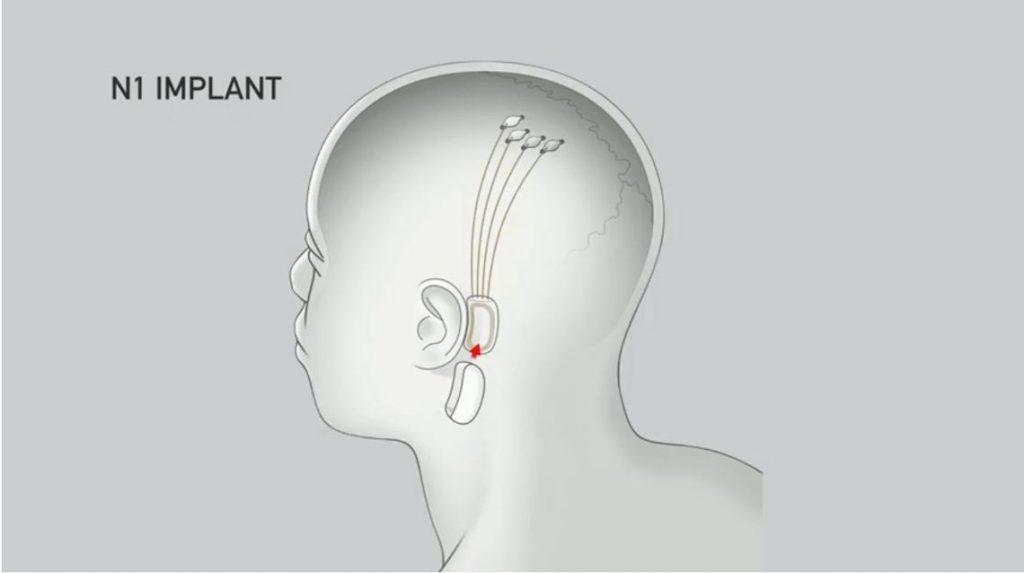
The n1 chip reads analogue brain signals amplifies them, digitizes them processes them and then sends it out to a pot device behind the ear. The pod device is the only thing that’s going to be upgraded. As soon as you remove the pod and everything shuts off!
The n1 chip is 4 by 5 millimetres low-power and has built-in hardware for processing brain signals. It can read 20,000 brain samples per second so these are real raw signals coming from a neural link hooked up to a brain.
What the scientists are looking for spikes and voltage when a neuron fires, is the fundamental element of communication within the brain. An algorithm can detect these spikes in real-time decode them and make sense of the vast amounts of data coming in the system. It can not only read data from the brain but also write data to do this.
A signal is run through an electrode near a neuron causing that neuron to fire. This kind of thing again isn’t new and has been done since the late 1950s it’s actually the basic technologies behind the cochlear implant the one that helps restore hearing the information inputted into the brain doesn’t have to be perfect because of neuroplasticity. This means that the brain learns how to use the new information reading data from the brain and inputting data into the brain can be and already kind of has been used to treat things like Parkinson’s and epilepsy but future applications can include things as far as depression and chronic pain!
The plan and the application
The original plan for the neural link is to connect for n1 chips with thousands of electrodes and coming from each chip signals will be sent via Bluetooth to the pod device behind the ER and it will be controlled by phone. The first goal is to get patients to be able to control a mobile device a phone mouse or computer keyboard. The neural link will show up as a regular Bluetooth keyboard or mouse they want to make people fully independent of their caretakers. This sounds lofty but has already been done before with a technology called the Utah Rae with only just a hundred electrodes patients are able to text other people and control tablets with their mind.
Remember the neural link has thousands of electrodes resulting in a cleaner more reliable signal for more complex applications. The first application for the neural link is to tap into the primary motor cortex the part of the brain that sends signals down to the spinal cord and onto the muscles to drive the movement.
It will start with simple things like a mouse and keyboard but could also be used to read signals from all movement even speech and finally, it could be used to restore movement of someone’s own body. The materials science team wants to use materials or properties that would make the brain not only accept the neural link but think that it’s part of itself. The team has already released a paper of reading recording and studying data from brains using their n1 chip it’s fairly controversial but early tests on monkeys have been successful as well. Monkeys have been able to control the computer with his brain. There it goes but human patient trials are set to start by the end of 2020 the target patient will be a quadriplegic due to a spinal cord injury.
The main hurdle so far has been FDA approval for implantable devices so the future of neural link will be in three stages.
Stage one is to understand and treat brain disorders starting with people with a serious medical need
Stage two is to preserve and enhance one’s own brain
Stage three focusses on full brain-machine interfaces in the future that could even be a kind of app store for programs that you can download and control with your brain.
Other possibilities from the presentation include a new kind of communication which is some kind of like telepathy or downloading the memories of someone who’s familiar with a city so that when you go to that city you feel familiar with it too.
Summary
The possibility is a kind of endless but of course, these are the very early days and we hardly understand anything about the brain right now although what the neural link is basing itself off has already been done in the medical field for decades. What they’re proposing is a giant leap above all of that and it’s going to be a long road to get there! The obvious questions remaining is this ethical should we do this? What about the risks?
So what do you guys think? Do you think it’s an interesting idea and should be pursued or do you have some kind of reservations? We are going to leave our opinion out of this and let you decide!
Follow this link, if you are looking to learn data science online!
You can follow this link for our Big Data course! This course will equip you with the exact skills required. Packed with content, this course teaches you all about AWS tools and prepares you for your next ‘Data Engineer’ role
Additionally, if you are having an interest in learning Data Science, click here to start the Online Data Science Course
Furthermore, if you want to read more about data science, read our Data Science Blogs

