Source: medium.com
Machine Learning is the latest buzzword in the analytical eco-space. The idea was there before as well but its usage has largely increased in recent times due to the enormous amounts of data that is available and the huge computational capacity of the modern systems.
Machine Learnings is the study of identifying patterns in the data by the system to make predictions on the new set of data. Several algorithms are programmed for this purpose and only the correct usage of such methods based on the problem statement in hand would lead to an accurate prediction.
The study of Machine Learning is divided into Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement learning. In Supervised learning, the output is labeled whereas unsupervised learning deals with an unlabeled dataset. In the case of Reinforcement learning, the learner is rewarded with prizes when made a correct decision and penalized for any incorrect move.
There are several algorithms used to make predictions. Some of them Linear, and Logistic Regression, Tree-Based algorithms like Decision Tree, Random Forest, Ensemble methods like Gradient Boost, XGBoost, and so on. Apart from these basic algorithms, there is a branch of Machine Learning which works on the concept of neural networks called Deep Learning.
Deep Learning is the advanced form of Machine Learning which requires more data and higher computational capacity. Some of the frameworks of Deep Learning are TensorFlow, Keras, Theano, PyTorch, etc.
Machine Learning is used by professionals of several fields like Banking, Insurance, Healthcare, and Manufacturing, to make predictions pertaining to several use cases in their respective fields. In this blog post, we would delve one of the use cases in the Transactional analytics field where Machine Learning has made several ground-breaking achievements.
What is Meant by Transactional Analytics?
The application performance, the outcome of the business, and the users are connected real-time through a mechanism known as Transactional Analytics. The real-time data gives insights on the customer experience, business outcomes after it is collected and correlated.
Transactional Analytics could be used to answer several questions about the performance of the business, and the KPI’s in real time. A correlation between the business and the performance data would ensure business growth, and the automated data gathering would provide time to value.
Moreover, the application performance could be optimized if the hundred percent of the business transaction is automatically collected, and correlated. Details of every business transactions of the application need to be captured, and its performance needs to be analyzed. The relationship between the data about a particular application should be auto-correlated to optimize the performance of that application.
How Transactional Analytics has helped in the growth of the business?
The rapid rise in the usage of the internet has resulted in the generation of unprecedented amounts of data. The sources of the data are endless and modern tools and technologies are equipped to handle large volumes of unstructured data as well which often carries more insights than structured data. Any organization could leverage the massive potential of big data to achieve real-time insights which would lead to the growth of the business.
Usage of Machine Learning for Transactional Analytics
Machine Learning has been implemented in several transactional systems to ease the process of the operation. Starting from Fraud detection systems to analyzing real-time high volume user information to drive riveting customer experiences, Machine learning has helped businesses to flourish. Here, we would look into one such use case where Machine Learning is implemented in Transactional Analytics.
The life Value of Customer Against its Acquisition Cost
The understanding of the transactional behavior of a customer is one of the key criteria for the growth of any business. In today’s world, there is no shortage of offers for customers for acquisition, and retention due to the large of small-scale companies that are emerging gradually. The behavioral analysis of a customer had become complex in recent times due to the enormous amounts of data and the arrival of several new business houses. However, modern technologies and tools do possess the power to leverage such terabytes of data to ensure customer satisfaction.
Collecting different sorts of data like operation cost, revenue growth, etc. could the profit trends of the customer, but it would not answer questions like the amount of money a business needs to spend to acquire a new customer or the true present value of a new customer.
To simplify the understanding, to understand new customer value, his cash flow patterns, and the customer’s longevity with the business need to be known. Suppose, a customer generates twenty-six dollars in two years, and two hundred sixty-four dollars in five years, then in ten years, his net worth would be seven hundred and sixty dollars.
Thus spending such huge amount of money at the start for a customer who would stay for ten years is not wise as the profit might vary in the future. On such scenarios, discount computing could be used which would cut the value from seven hundred and sixty dollars to three hundred and four dollars at fifteen percent discount rate. This amount is viable as the company could pay three hundred and four dollars for a customer who would stay for ten years on acquisition costs.
Once the amount is calculated, the next hurdle is to find the longevity of the customer in the company. The answer to these questions lies within the retention rates which is dependent upon age, gender, and so on. The best way to calculate the average stay of a customer is to get the count of the number of customers who would defect to find the defection rate and then invert the fraction.
The customer lifetime calculation leads to the question of customer cash flow. Assuming that the defection rate is constant which never happens in real life as the rate is generally much higher in the initial years and decreases gradually. On top of this assumption, we need to calculate the classes of the customer at different cycles instead of individual customer value one by one as companies invest in a set of customers during acquisition.
Imagine a scenario where one lakh new customers enter at a particular time, and the company invests eighty dollars at that particular time which would take the amount to eight million dollars for the entirely new group of customers. Now, after a year, say twenty-two percent of the customer’s defects and leaves behind the remaining seventy-eight percent to pay back the eight million dollars invested initially. After five years, if more than half of the customers joined defects, then the cash flow till of the time of defect is estimated.
Previously, we set three hundred and four dollars as customer value. Now, if the defection rate continues to be at ten percent, then it would be dangerous to decide the money invested as at this rate the number would reduce to hundred and seventy-two dollars from three hundred and four dollars.
The scope of Machine learning is quite feasible in this regard. So far, we tried to find the longevity of the customer and its lifetime value which got decreased from $ 760 to $172. Still, it contains some distinct human behaviors which need to be taken into the account. The marketing campaign based on machine learning to target a customer could also allow calculating every unique customer’s lifetime value.
It could also be added that various dependent variables make it difficult to get the correct accounting number as more and more transactional data is generated. There are various factors which influence the transactional behavior of customers, and using machine learning model would create a probabilistic metric which could help the business to make economic predictions going forward.
Conclusion
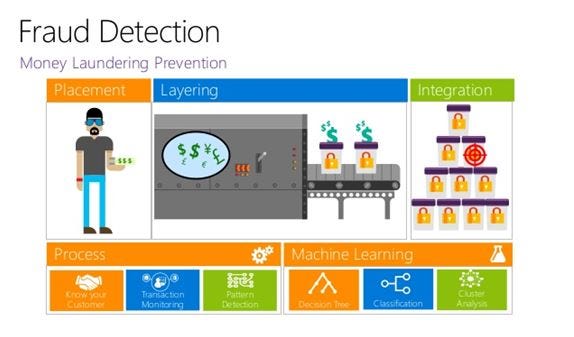
This was one of the use cases where Machine Learning plays a major role in improving the transactional business. One of the other usages of Machine Learning in Transactional Analytics is in Fraud Detection.
In this case, the system could understand patterns from the customer’s purchased data and predict the fraud in the new set of transactions based on the concept of cognitive computing. Machine Learning ensures the confidence level is high while deciding on a transaction. It also allows the evaluation of multiple transactions in real time.
With an increased number of transactions, the models tend to perform better. It maintains efficiency and often acts better than humans in dealing with fraudulent behaviors.
The fraud detection process starts with gathering the relevant data and perform exploratory data analysis on the data to get rid of noise from the data. It is then divided into training, testing, and validation data sets. Once the data set is ready, it is then fed to several classification algorithms like Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, and even neural networks which are fast and more efficient than conventional Machine Learning algorithms.
However, there are few drawbacks in Fraud Detection using Machine Learning such as Lack of inspectability, the possibility of overlooking some obvious activities like card sharing.
Machine Learning has a wide range of usage in the Transactional analytics and in this article we have seen a couple of such use cases. Dimensionless has several blogs and training to get started with Machine Learning and Data Science in general.
Follow this link, if you are looking to learn more about data science online!
You can follow this link for our Big Data course!
Additionally, if you are having an interest in learning Data Science, Learn online Data Science Course to boost your career in Data Science.
Furthermore, if you want to read more about data science, you can read our blogs here
Read our Recent Blogs,
