Introduction
Amazon Web Services (AWS) was the first significant player to offer reasonably priced cloud infrastructure and services, and it continues to be the single largest vendor in the cloud market. With AWS, businesses have access to extremely durable storage, cost-effective compute power, high-performing databases and more without the hassle of provisioning and managing infrastructure. AWS services are available without any up-front investments, and you pay for only what you use.
ETL is one of the primary tasks in the analytics industry. You can do ETL in AWS in a few different ways:
- AWS Glue
- Data pipeline
- A custom solution, e.g. a Docker
In this blog, we are going to focus the ETL part through AWS Glue. We will also look at components of AWS Glue. Furthermore, we will try to play with AWS glue a bit in order to understand it in depth.
What is AWS Glue?
AWS Glue is a fully managed ETL (extract, transform, and load) service that makes it simple and cost-effective to categorize your data, clean it, enrich it, and move it reliably between various data stores. It consists of a central metadata repository known as the AWS Glue Data Catalog, an ETL engine that automatically generates Python or Scala code, and a flexible schedule that handles dependency resolution, job monitoring, and retries. Also, AWS Glue is serverless, so there’s no infrastructure to set up or manage.
Use the AWS Glue console to discover data, transform it, and make it available for search and querying. The console calls the underlying services to orchestrate the work required to transform your data. You can also use the AWS Glue API operations to interface with AWS Glue services. Edit, debug and test your Python or Scala Apache Spark ETL code using a familiar development environment.
AWS Glue Components
AWS Glue provides a console and API operations to set up and manage your extract, transform, and load (ETL) workload. You can use API operations through several language-specific SDKs and the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI)
AWS Glue uses the AWS Glue Data Catalog to store metadata about data sources, transforms, and targets. The Data Catalog is a drop-in replacement for the Apache Hive Metastore. The AWS Glue Jobs system provides a managed infrastructure for defining, scheduling, and running ETL operations on your data.
AWS Glue Console
You use the AWS Glue console to define and orchestrate your ETL workflow. The console calls several API operations in the AWS Glue Data Catalog and AWS Glue Jobs system to perform the following tasks:
- Define AWS Glue objects such as jobs, tables, crawlers, and connections.
- Schedule when crawlers run.
- Define events or schedules for job triggers.
- Search and filter lists of AWS Glue objects.
- Edit transformation scripts.
AWS Glue Data Catalog
The AWS Glue Data Catalog is your persistent metadata store. It is a managed service that lets you store, annotate, and share metadata in the AWS Cloud in the same way you would in an Apache Hive metastore.
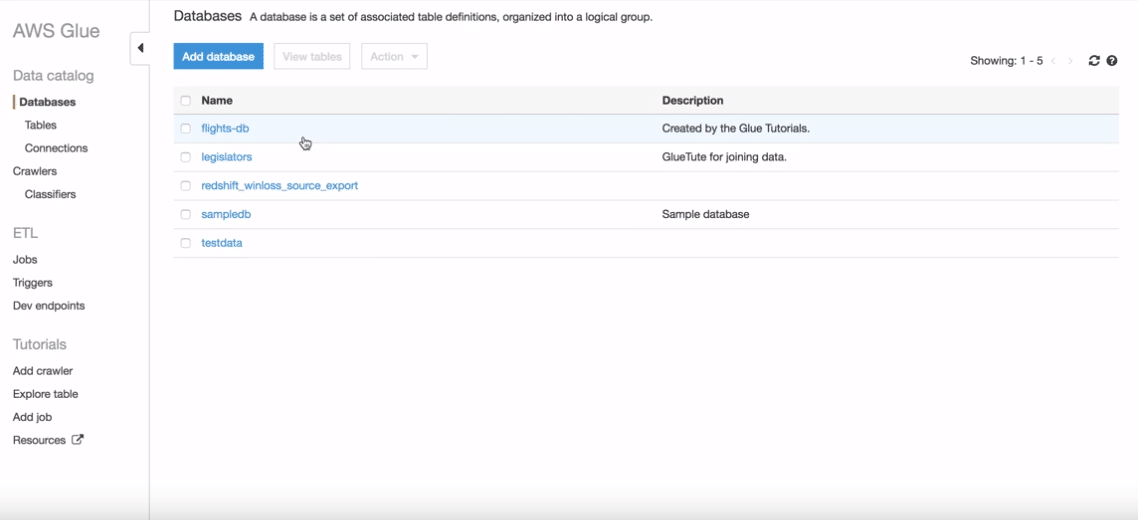
Each AWS account has one AWS Glue Data Catalog. It provides a uniform repository where disparate systems can store and find metadata to keep track of data in data silos and use that metadata to query and transform the data.
You can use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to control access to the data sources managed by the AWS Glue Data Catalog. These policies allow different groups in your enterprise to safely publish data to the wider organization while protecting sensitive information. IAM policies let you clearly and consistently define which users have access to which data, regardless of its location.
AWS Glue Crawlers and Classifiers
AWS Glue also lets you set up crawlers that can scan data in all kinds of repositories, classify it, extract schema information from it, and store the metadata automatically in the AWS Glue Data Catalog. From there it can be used to guide ETL operations.
AWS Glue ETL Operations
Using the metadata in the Data Catalog, AWS Glue can autogenerate Scala or PySpark (the Python API for Apache Spark) scripts with AWS Glue extensions that you can use and modify to perform various ETL operations. For example, you can extract, clean, and transform raw data, and then store the result in a different repository, where it can be queried and analyzed. Such a script might convert a CSV file into a relational form and save it in Amazon Redshift.
The AWS Glue Jobs System
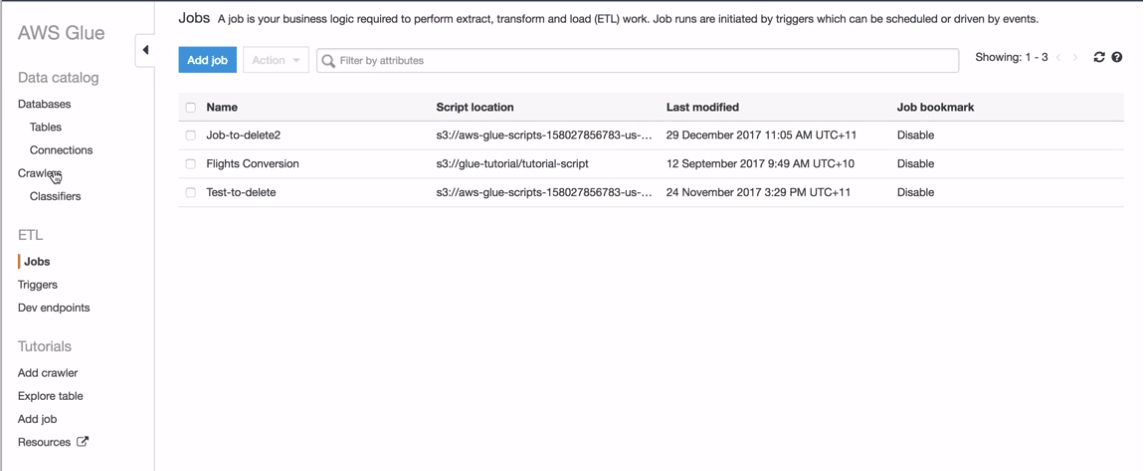
The AWS Glue Jobs system provides managed infrastructure to orchestrate your ETL workflow. You can create jobs in AWS Glue that automate the scripts you use to extract, transform, and transfer data to different locations. Jobs can be scheduled and chained, or they can be triggered by events such as the arrival of new data.
Importing Metadata and Running Crawlers
In this section, we will be importing data table and it’s metadata from Amazon redshift to Glue. We will be using the crawler features present in the Amazon Glue to import the data. So let us start importing!
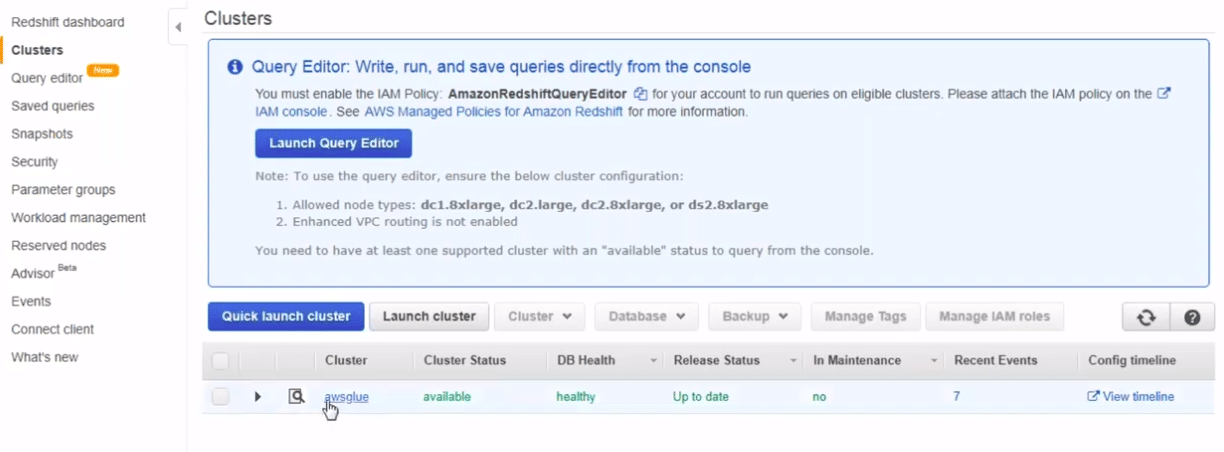
First, we will go to our redshift cluster and navigate to the database. From there, we will navigate to our final table.
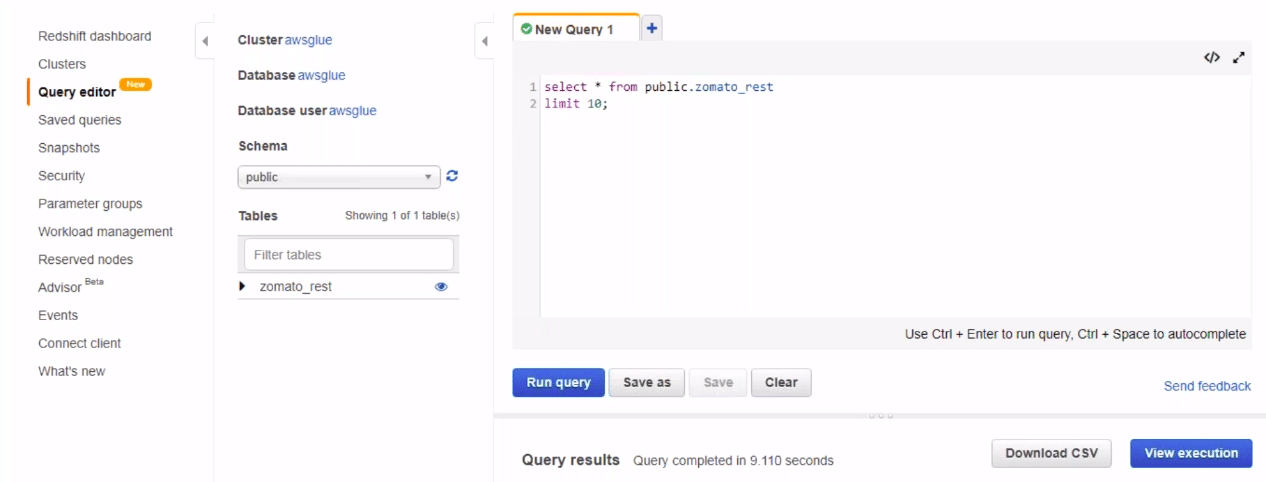
We can try running the query to view the data. We will view all the components of the data which we need to export to Glue.
Once we have our data, we can go to AWS Glue and select add connection feature.
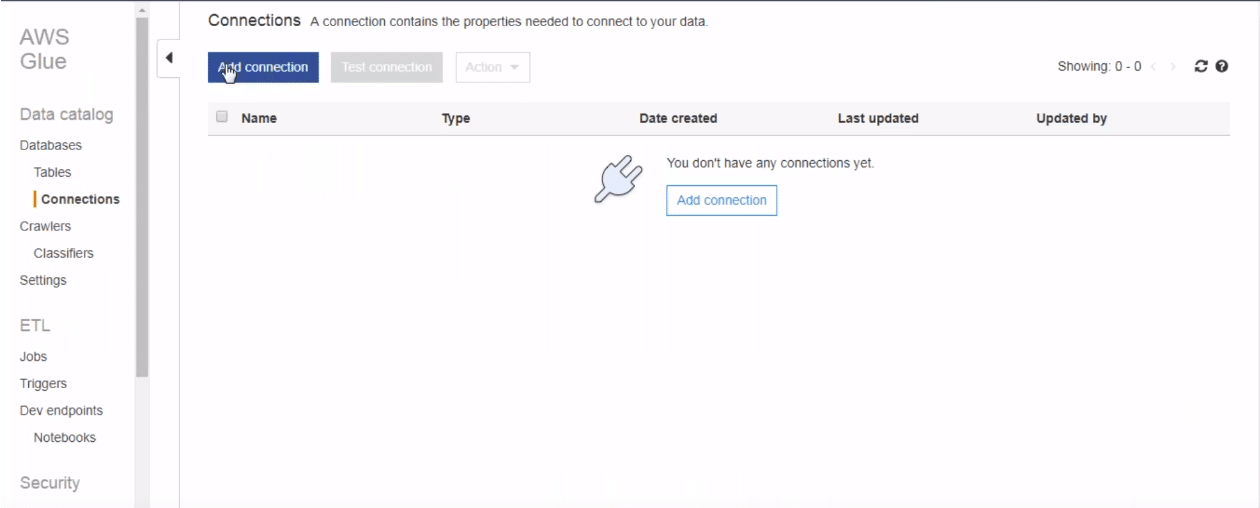
After clicking add the connection, we need to mention the various attributes to set up the connection. You need to mention the connection name and type. Since we are importing from redshift, we mention redshift here. We follow a similar process to fill the remaining setup.
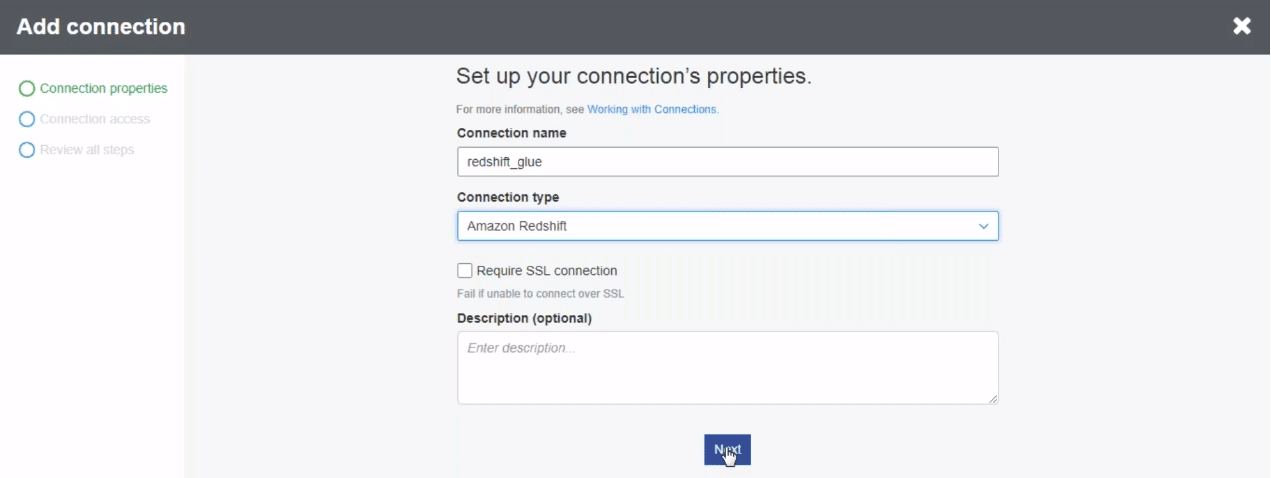
Click next to set up the connection!
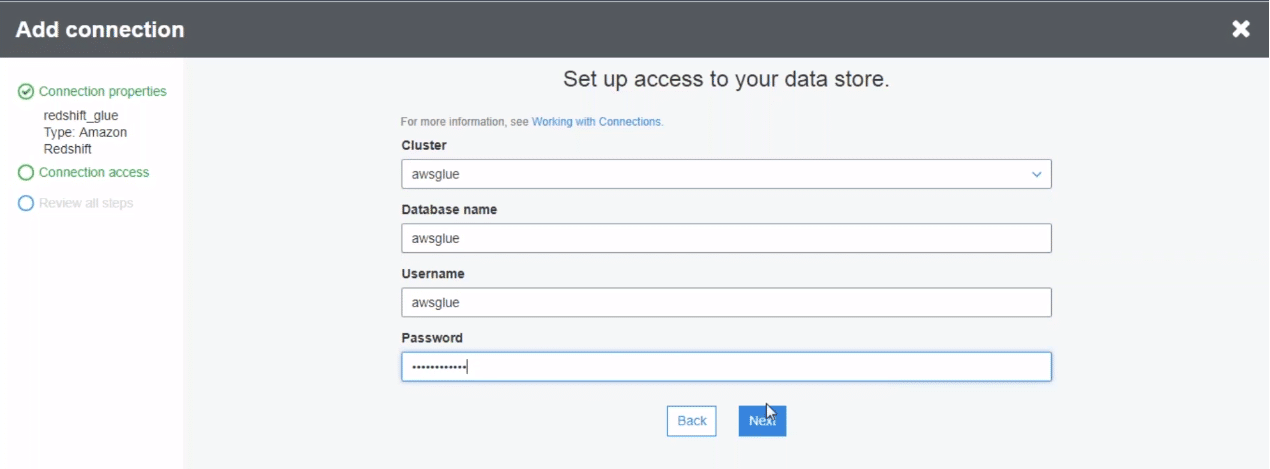
Once, you click next, AWS starts setting up the connection to the redshift. Once the connection is there, you can see it on your console.
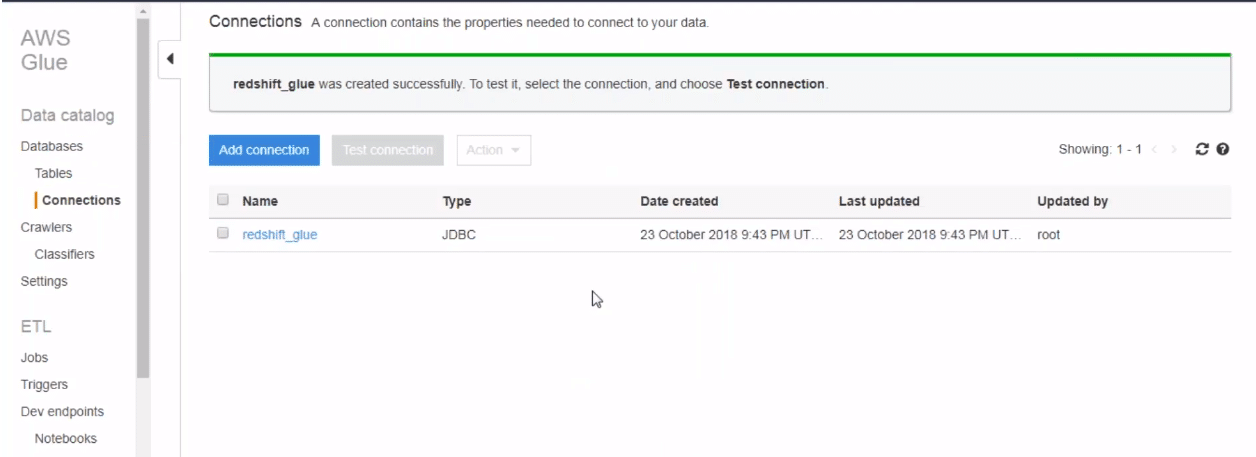
Now we need to set up a crawler to get the data from redshift to the Glue. Similar to add a connection, we fill different attributes of the crawler here
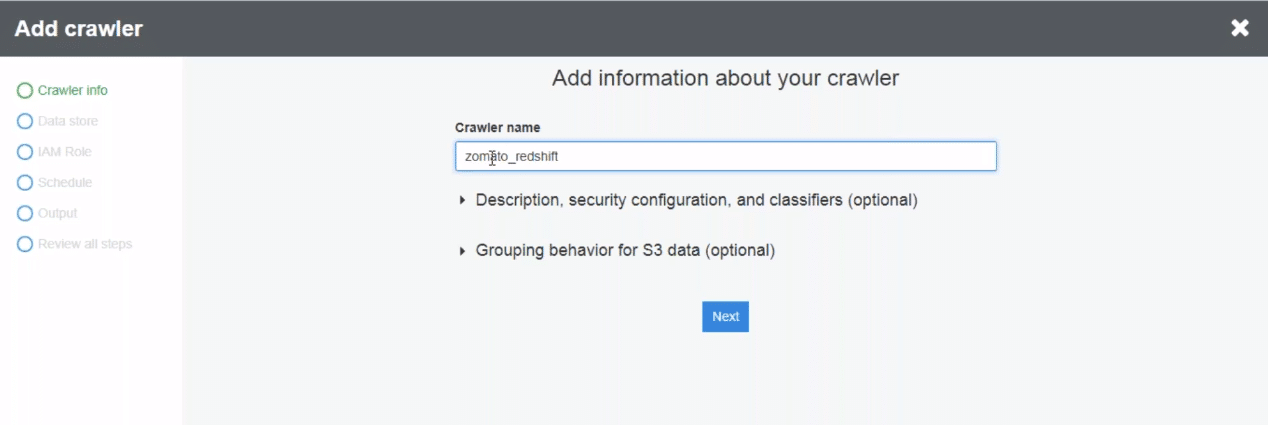
You need to mention parameters like the database to read, the table to read, connection type etc to set up the crawler. Once we have all the parameters filled, we can click next to set up the crawler.
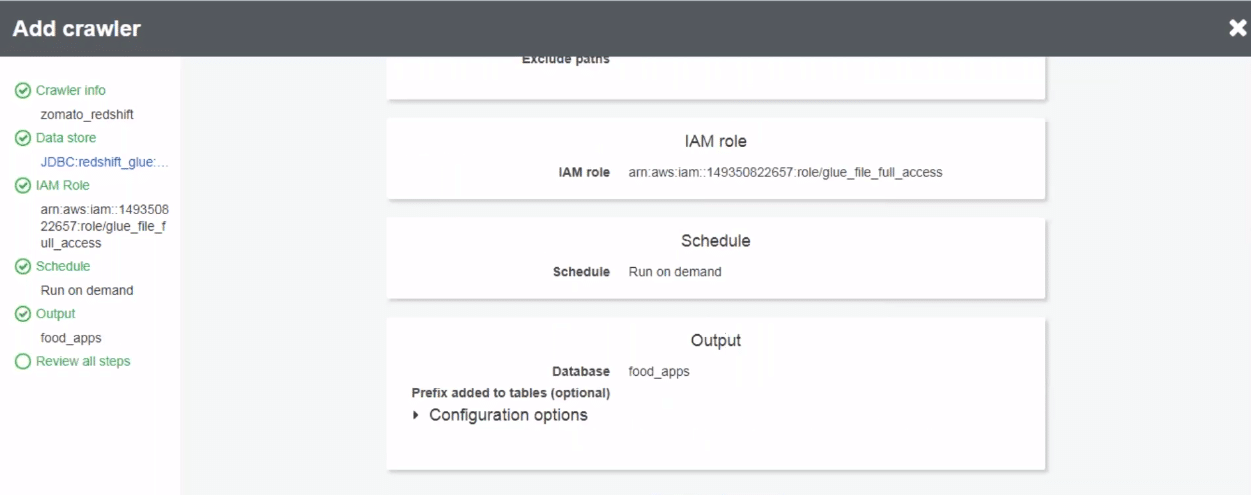
As you can see in the below screenshot, after clicking next, the crawler is setup. All we need to do now is run it. Click on “run it now” button. Upon clicking the button, AWS runs the crawler. Once the crawler task finishes, it stores all the data from redshift to Glue.
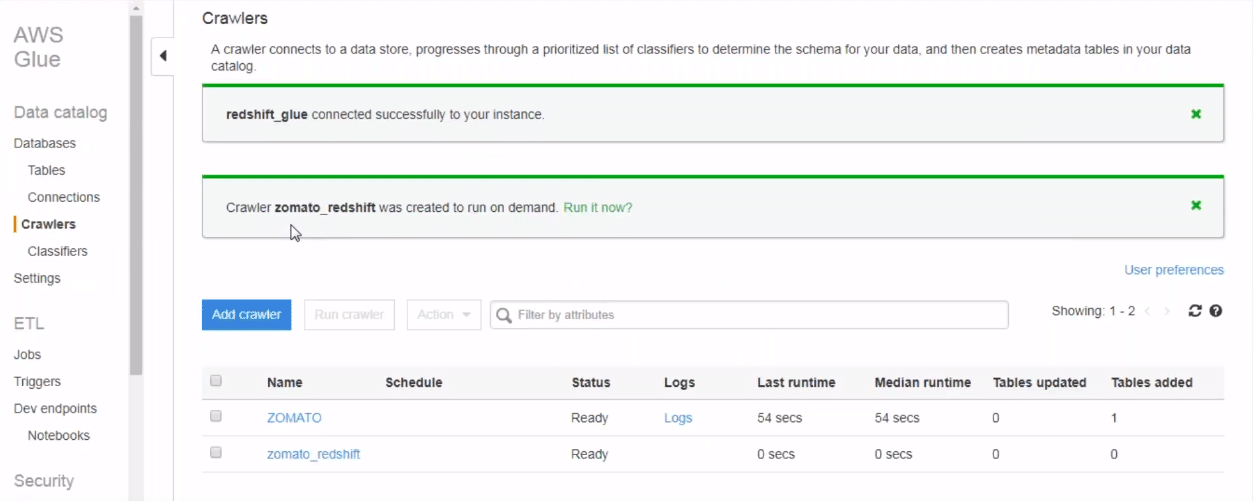
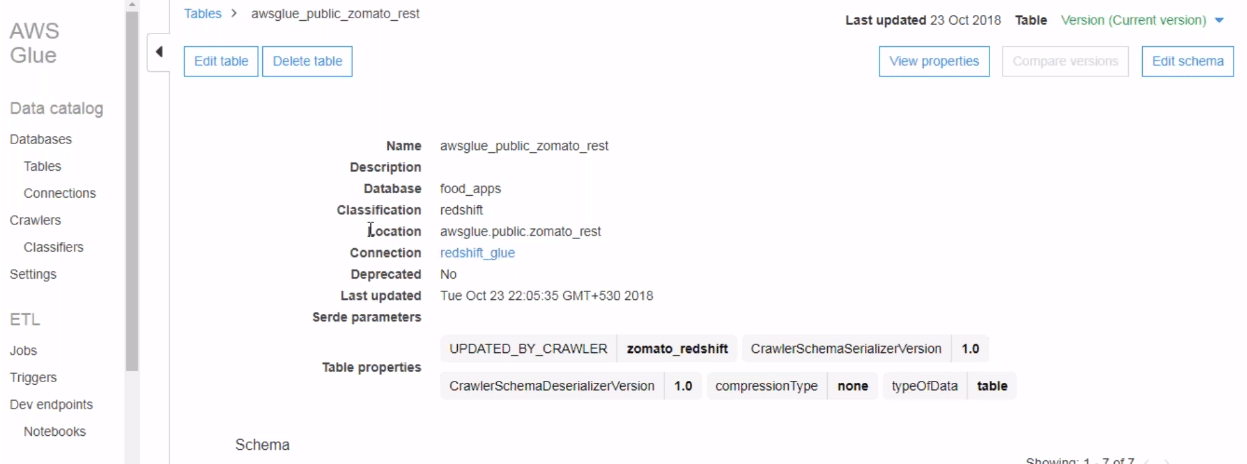
You can actually view the imported tables. Also, you can go to the tables and then you can see your specific table created there. Now click on the table to view the properties and the schema
Writing and Triggering Scripts in Glue
A script contains the code that extracts data from sources, transforms it, and loads it into targets. AWS Glue runs a script when it starts a job.
AWS Glue ETL scripts can be coded in Python or Scala. Python scripts use a language that is an extension of the PySpark Python dialect for extract, transform, and load (ETL) jobs. The script contains extended constructs to deal with ETL transformations. When you automatically generate the source code logic for your job, a script is created. You can edit this script, or you can provide your own script to process your ETL work.
To make a script, click on jobs in AWS Glue. You can make a new script here. In this case, we are editing our old one. Click on the script/job and a sample pop up will come. To edit the script, you can click “edit script”.
Edit script option gives you a full editor view to manage the job. The job is more again like ETL operations which you want to perform on the moving data.
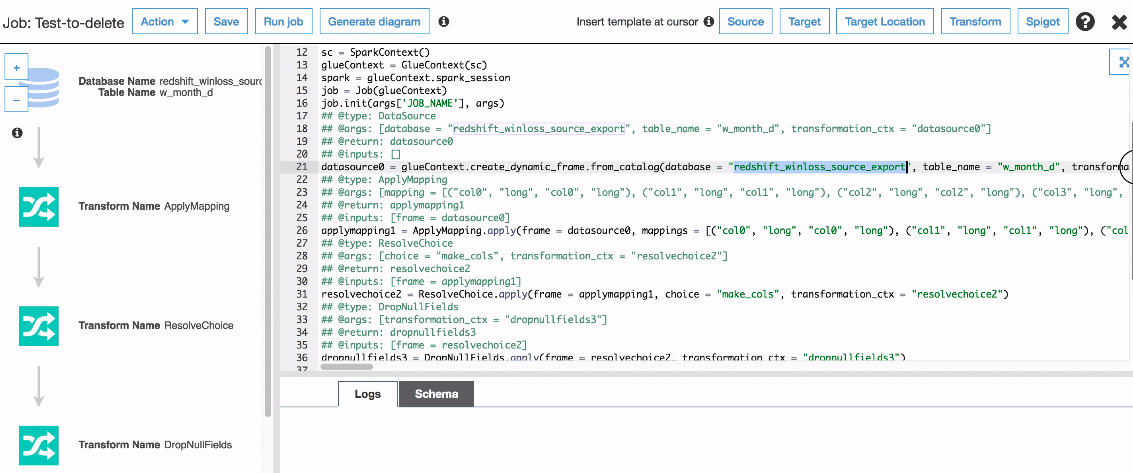
There can be cases when you want your jobs to happen in a sequence. you can use triggers. Triggers can run the code upon receiving some action. For example, you may want a script to run once a prev script has finished the execution. In the screenshot below too, you can see how delete job is mapped to completion trigger of some other job. Once that previous job finishes execution, only then delete job will start the execution
Summary
I’ve used a custom solution for a while but recently decided to move to Glue, gradually. Why? Because when it is set up, you have so much less to worry about. Glue is the preferred choice when you need to move data around. If you’re unsure what route to take, stick to Glue. If you find it doesn’t fit your needs well, only then look elsewhere.
Follow this link, if you are looking to learn more about data science online!
You can follow this link for our Big Data course!
Additionally, if you are having an interest in learning Data Science, click here to start Best Online Data Science Courses
Furthermore, if you want to read more about data science, you can read our blogs here

